外文期刊|农田基流冲刷富含有机质的沙质土壤加剧洱海的非点源污染
来源:农业人才网
时间:2023-09-10
08:34:34
作者:农业人才网
浏览量:

作者:Debo He;Xianglong Liu;Yan Fu;Tao Wang;Bo Zhu
作者背景:Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610041, China;Key Laboratory of Mountain Surface Process and Ecological Regulation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu 610041, China;University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
论文题目:Field Baseflow Eluting SOM-Rich Sandy Soil to Exacerbate Non-Point Source Pollution of Lake Erhai, Southwest China
DOI:10.3390/HORTICULTURAE9080898
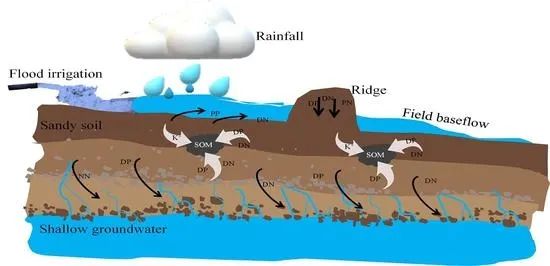
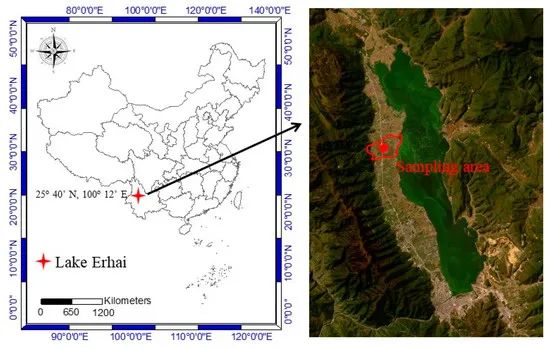
洱海西岸农田养分流失严重,导致洱海流域非点源污染严重。然而,由于土壤性质和环境因素的复杂性,缓解这一问题具有挑战性。在洱海流域雨季期间,我们采集并分析了土壤剖面样品、35个表层土壤( 0 ~ 20 cm)样品和300多个野外基流样品。本研究的目的是探究土壤性质、田间基流和农业管理措施对养分时空迁移的影响。结果表明,土壤有机质( SOM )含量对沙地土壤养分空间分布格局有显著影响。因此,这导致洱海流域营养盐流失的潜力大幅降低。在高施肥和大水漫灌条件下,菜地基流表现出最高的氮磷浓度。与无降雨时期相比,降雨期间基流中TN和TP浓度分别增加了2倍和7.7倍。优化农业措施,如有机肥替代化肥、改变灌溉方式等,提高沙土有机质含量,尽量减少基流冲刷,对缓解洱海流域农业面源污染具有有利影响。研究结果可以使我们对洱海流域非点源污染问题有更系统的认识,为制定有针对性的农业非点源污染减排方案提供理论依据。同时,优化农业经营模式,平衡农业经济发展与生态保护问题,对管理者具有重要的现实意义。Excessive nutrient loss from farmland located on the west bank of Erhai Lake has resulted in significant non-point source pollution within the Lake Erhai basin. However, mitigating this issue proves challenging due to the intricate nature of soil properties and environmental factors. Here, during the rainy season in the Lake Erhai basin, we collected and analyzed soil profile samples, 35 topsoil (0–20 cm) samples, and more than 300 field baseflow samples. Our objective was to explore the influences of soil properties, field baseflow, and agricultural management measures on the spatiotemporal migration of nutrients. The results indicated that the concentration of soil organic matter (SOM) has a significant impact on the spatial patterns of nutrient distribution in sandy soil. Consequently, this leads to a substantial reduction in the potential for nutrient loss in the Lake Erhai basin. The vegetable-field baseflow exhibited the highest concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus when subjected to high fertilization and flood irrigation. The concentrations of TN and TP in baseflow increase by a factor of 2 and 7.7, respectively, during rainfall compared to periods of no rainfall. Optimizing agricultural measures, such as replacing chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers and modifying irrigation methods to enhance the organic content of sandy soil and minimize baseflow elution, has a beneficial impact on mitigating agricultural non-point source pollution in the Erhai Lake basin. The research results can enable us to have a more systematic understanding of the problem of non-point source pollution in the Erhai River Basin, and provide a theoretical basis for developing targeted agricultural non-point source pollution mitigation plans. Simultaneously, optimizing agricultural management models to strike a balance between agricultural economic development and ecological protection issues holds significant practical significance for managers.看更多洱海科技论文
你若喜欢,点赞点在看哦